The modular construction market has experienced a massive surge of growth over the past few years, reaching a value of $76 billion in 2021.
While modular construction currently represents a small subset of the $1 trillion construction industry, the market will only continue to grow as demand increases. More people than ever are turning to prefabrication for its on-site efficiency, improved labor productivity and safety and lower construction costs.
In addition to these benefits, modular construction represents a huge leap forward in environmental sustainability, including excellent opportunities for more responsible use of building materials and more eco-friendly designs.
Read on to learn more about the benefits of modular construction and how it works, or jump to our infographic to get a visual look at the eco-friendly features of modular buildings.
What Is Modular Construction?
Modular construction is a process that involves constructing prefabricated buildings in off-site factories and transporting them to a worksite for installation. While modular structures meet the same building codes and regulations as traditional buildings, they consist of smaller prefabricated units, called modules, which are assembled after arriving at a worksite.
- In the factory, modules are built using assembly line systems and construction technology, leading to an efficient and standard process. The use of precise modeling and construction in the factory reduces the need for change orders and adjustments.
- Before leaving the factory, walls, floors, roofs, doors, and windows are built and installed, and wiring, plumbing, and ductwork are added. Many modern modular buildings are even outfitted with fixtures and finishes before leaving the factory.
- Once the modules are built, they are transported to the building site on flatbed trucks and assembled in a predetermined order, a process that uses cranes to set the modules in place onto a preset foundation.
- After the modules are set in place, construction professionals seamlessly fit them together to create a unified building. The resulting structures are often finished twice as fast as similar buildings on traditional sites.
Types of Modular Buildings
Permanent
Permanent modular construction (PMC) involves building prefabricated modules off-site, delivering them to the worksite, and assembling them to create a permanent structure. These buildings are highly customizable and come in many shapes and sizes. Professionals can use PMC to build anything from single-story homes to residential high rises.
Relocatable
Relocatable modular buildings are unique in that they can be moved from one location to another after the initial installation. Professionals either partially or fully assemble these structures in an off-site facility, then transport them to the building site. Because relocatable buildings are cost-efficient and easy to move or repurpose, they’re a popular option for construction-site offices, schools, medical facilities, and other organizations that need a temporary structure.
Benefits of Modular Construction
Not only do modular buildings take less time to build, but they also offer many other advantages to construction crews, building owners and the environment. These benefits begin in the factory and continue throughout a building’s lifetime.
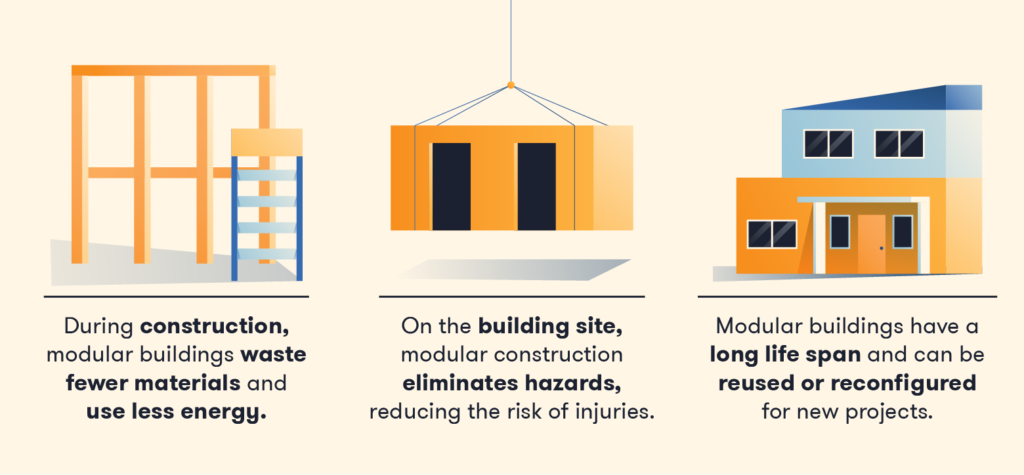
1. Decreases Construction Waste
Traditional building methods generate around 56 million tons of debris every year, while modular construction uses precise planning and measurements to reduce the risk of mistakes and wasted materials. Multiple modules are also created simultaneously during this process, so any materials that would otherwise be discarded can be reused for other projects in the same facility.
2. Uses Recycled Materials
Modular buildings use a variety of sustainable materials, many of which are recycled. Repurposed materials like wood, steel, and aluminum can form siding, frames, and roofs. Some modular construction companies also use innovative materials like oriented strand board (OSB) made from fast-growing, sustainably sourced wood. Modular design professionals are getting increasingly creative with sustainable materials in their buildings. For example, Wikkelhouses are made entirely of recycled cardboard and are expected to last for 100 years.
3. Decreases Energy Consumption
Since construction happens in a controlled factory setting, producing a modular structure uses less energy. During construction, energy usage is optimized using machine learning to create an environmentally sound building process, and shorter construction times result in lower on-site energy expenditures. Professionals can also install structural insulated panels in modular buildings to better maintain their internal temperature and reduce the need for heating and air conditioning.
4. Reduces Emissions
A United Nations report from 2017 found that 39% of global carbon emissions result from the construction field, much of which results from inefficient material and labor transportation. By reducing trips to and from the job site and optimizing module delivery, modular construction can reduce total deliveries to building sites by 90%, which greatly reduces total emissions. Additionally, many modular buildings are equipped with solar panels to lower carbon emissions for the lifetime of the building. A simple solar setup can prevent 2.5 tons of carbon emissions annually.
5. Features Green Fixtures and Finishes
6. Built To Last — And Be Reused
Modular building designs have a distinct advantage when it comes to resilience and long life spans, but this can also be true of many traditional buildings. Unique to modular buildings is the ease with which they can be disassembled — to be either reused in other locations and configurations or recycled for new projects. When considering long-term sustainability, reusable modular buildings help reduce debris generated by demolition, which accounts for more than 500 million tons of waste each year.
7. Improves Worker Safety
Because much of the building process takes place indoors in a controlled environment, modular construction greatly reduces the risk of falls and other work-related injuries. This is an important advantage in an industry plagued by a high work injury and mortality rates. Less on-site work protects workers from dangerous weather conditions, eliminates hazards, and lowers the risk of fatigue.
8. Lowers Project Costs
Shorter construction times, fewer transportation and labor costs, and less expensive materials make modular construction more cost-effective than traditional building methods. As technology continues to advance and the process becomes more efficient, project owners may even see further opportunities to reduce costs in the future.
What Are the Drawbacks?
1. Risk of Damage During Transport
2. Limited Design Options
Modular buildings are fast and efficient to build, but they often have fewer customization options than traditional structures. Construction professionals stack repetitive and uniform modules to build structures like apartment buildings, hotels, and homes. Creating more unique modules would require much more time, money, and resources, eliminating many of the benefits of modular construction.
3. High Upfront Costs
4. Fewer Suppliers
The Future of Modular Construction

Thanks to growing demand in health care, affordable housing, and many commercial industries, the global modular construction market will experience a 6.4% annual growth rate over the next six years.
Prefabrication allows for quicker and more cost-effective building processes, which could help alleviate the current affordable housing crisis. The efficiency of modular construction could be necessary as construction sites adapt to industry changes in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic.
Modular construction technology is a powerful remedy for many challenges facing today’s construction industry, like high costs and labor shortages. Importantly, though, modular construction also has a beneficial effect on the environmental impacts of construction and encourages building designs that utilize green energy for a more sustainable future.
